Number System Class 10 Computer Science
Introduction
Many years ago, the concept of a number system evolved
when people used their fingers, sticks, pebbles, knots of rope, and different
symbols for counting and simple addition or subtraction. In course of time,
people use calculator devices and then computers for calculation. The group of digits or symbols used to
express quantities as the basis for doing different calculations is called the number system.
Types of Number System
Nowadays, different types of number systems have
developed. The number system is differentiated by its base or radix. The base is
defined as the total number of digits available in the number system. So, the
number system is divided into main four types on the basis of the base value. They
are:
1. Decimal
number system
2. Binary
number system
3.
Octal number system
4.
Hexadecimal Number System
 |
| Number System |
1. Decimal Number System
The number system that we use in our day to day life is
the decimal number system.
The decimal number system has a base 10 as it uses 10 digits
from 0 to 9. In a decimal number system, the successive positions to the left of
the decimal point represents units, tens, hundreds, thousands, and so on.
Each position represents a specific power of the base
(10). For example, the decimal number 539 consists of the digit 9 in the unit’s
position, 3 in the tens position, and 5 in the hundreds position. Its value can
be written as
(539)10 =(5×100)+(3×10)+(9×1)
= (5×102) + (3×101) + (9×100)
= 500 + 30 + 9
= 539
2.
Binary
Number System
The number system that is used in computer systems to
hold any data on bits is the binary number system. The binary number system has
base 2 as it uses 2 digits 0 and 1. For example 100012, 111012,
1012, etc.
3.
Octal
Number System
The number system that is used in the computer system to
hold any data on byte is the octal number system. Octal number system has a base
8 as it uses 8 digits from 0 to 7.
For example 1208 , 65708 ,
320708 , etc.
4.
Hexadecimal
Number System
The number system that is used in
computer system to hold any data is the hexadecimal number system. Hexadecimal
number system has base 16 as it uses 16 digits (10 digits from 0 to 9 and 6
letters from A to F). Letters represent the numbers starting from 10 that is A
= 10, B = 11, C = 12, D = 13, E = 14 and F = 15. For example, (7A2)16, (1AC)16, (56B)16, (BOD)16 etc.
Number System Conversion
People commonly use decimal number system in their
daily life. Computer use binary, octal and hexadecimal number system according
to its model or brand. We cannot easily understand binary number system like
this way computer can't understand decimal number system. So there are
different methods to convert one number system to another as follows:
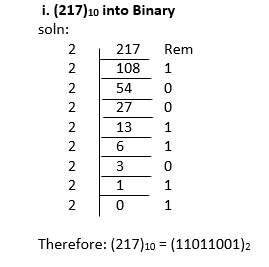
1. Decimal to Binary Number System
Conversion
To convert decimal number to binary number follows
the following steps:
a.
Divide the given decimal number by 2 and write
down the remainder.
b.
Divide quotient by 2 and again write down the
remainder.
c.
Repeat the process until the quotient becomes zero.
d.
Write the remainders from bottom to top.
Examples
2. Binary to Decimal Number System Conversion
To convert binary number to decimal number follows
the following steps:
 |
3. Decimal to Octal number system conversion
To convert decimal number to octal number follows
the following steps:
a.
Divide the given decimal number by 8 and write
down the remainder.
b.
Divide quotient by 8 and write down the
remainder.
c. Repeat the process until the quotient becomes zero.
d. Write the remainders from bottom to top.
5. Decimal to Hexadecimal Number System
Conversion
To convert decimal number to hexadecimal number follows
the following steps:
a.
Divide the given decimal number by 16 and write
down the remainder.
b.
Divide quotient by 16 and write down the
remainder.
c.
Repeat the process until quotient becomes zero.
d.
Write the remainders from bottom to top.
Binary Table
|
Decimal |
Hexadecimal |
Octal |
Binary |
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
2 |
2 |
2 |
10 |
|
3 |
3 |
3 |
11 |
|
4 |
4 |
4 |
100 |
|
5 |
5 |
5 |
101 |
|
6 |
6 |
6 |
110 |
|
7 |
7 |
7 |
111 |
|
8 |
8 |
10 |
1000 |
|
9 |
9 |
11 |
1001 |
|
10 |
A |
12 |
1010 |
|
11 |
B |
13 |
1011 |
|
12 |
C |
14 |
1100 |
|
13 |
D |
15 |
1101 |
|
14 |
E |
16 |
1110 |
|
15 |
F |
17 |
1111 |
7. Binary to Octal Number System Conversion
To convert binary number to octal number follows the
following steps:
a.
Arrange binary digits in group of three from
right to left.
b.
Write respective octal number for each binary
group.
c.
Give the result base 8.
Examples:
i.
(110010011)2 = (?)8
3 digits
combination = 110 010
011
Octal
Equivalent = 6 2 3
(110010011)2 = (623)8
Rough
4 2 1 4 2 1 4 2 1 (
Positive Powers of 2)
1 1 0
0 1 0 0 1 1
4 + 2
2 2 + 1 (Adding
the numbers for 1)
6 2 3
ii.
(100010011000)2 = (?)8
3 digits
combination = 100 010 011
000
Octal
Equivalent = 4 2 3
0
(100010011000)2 = (4230)8
Rough
4 2 1 4 2 1 4 2 1 4 2 1 (Positive Powers of 2)
1
0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0
4
2 2+1 0 ( Adding the numbers for 1)
4
2 3 0
8. Octal to Binary Number System
Conversion
To convert octal number to binary number follows the
following steps:
a.
Write the octal digits separately.
b.
Write
binary triple equivalent to each octal number.
c.
Give the result base 2.
Examples:
i.
(236)8 = (?)2
Octal
number = 2 3
6
Binary
equivalent = 010 011 110
(236)8 = (010011110)2
Rough
2
3 6 (Octal
Numbers
4 2 1 4 2 1 4
2 1
0 1 0 0 1 1 1
1 0 (3
bits equivalent Binary number) It is the sum of the digits that requires to
bring the octal number of the question) For example: 6 = 4+2+0 (Added numbers
are 1 and remaining 0)
ii.
(704)8 = (?)2
Octal
number = 7 0
4
Binary
equivalent = 111 000 100
(704)8 = (111000100)2
Rough
7 0 4
4 2 1 4 2 1 4 2 1
1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 (3
bits equivalent Binary number) It is the sum of the digits that requires to
bring the octal number of the question) For example: 4 = 4+0+0 (Added numbers
are 1 and remaining 0)
9. Binary to Hexadecimal number system conversion
To convert binary number to hexadecimal number
follows the following steps:
a.
Arrange binary digits in group of four from
right to left.
b.
Write respective hexadecimal number for each
binary group.
c.
Give the result base 16.
Examples:
i. (110010011)2 = (?)16
|
4
digits combination = 0001 |
1001 |
0011 |
|
Hexadecimal
equivalent = 1 (110010011)2 = (193)16 Rough 8
4 2 1 8 4 2 1 8 4 2 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0
0 1 1 1 8+1 2+1 1
9 3 ii. (10001001100)2 = (?)16 |
9 |
3 |
|
4
digits combination = 0100 |
0100 |
1100 |
|
Hexadecimal
equivalent= 4 (110010011)2 = (193)16 Rough 8
4 2 1 8 4 2 1 8 4 2 1 0
1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 4
4 8+4 1
9 12=C |
4 |
C |
10. Hexadecimal to Binary number system conversion
To convert hexadecimal number to binary number
follows the following steps:
a.
Write binary equivalent 4 digits’ group to each
hexadecimal number.
b.
Give the result base 2.
Examples:
i. (9A3)16 = (?)2
|
4
digits combination = |
0100 |
0100 |
1100 |
|
Hexadecimal number = |
9 |
A |
3 |
|
Binary
equivalent = (9A3)16
= (100110100011)2
Rough |
1001 |
1010 |
0011 |
|
8
4 2 1 8 4 2 1 |
|
8 4 2 1 |
|
|
9
A=10 |
|
3 |
|
|
8
4 2 1 8 4 2 1 |
|
8 4 2 1 |
|
|
1
0 0 1 1 0 1 0 ii. (B0D)16 = (?)2 |
|
0 0 1 1 |
|
|
Hexadecimal number = |
B |
0 |
D |
|
Binary
equivalent = (B0D)16
= (101100001101)2 Rough |
1011 |
0000 |
1101 |
|
B=11
0 |
D=13 |
|
|
|
8
4 2 1 8 4 2 1 |
8 4 2 1 |
|
|
|
1
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 |
1 1 0 1 |
|
|
11. Octal to Hexadecimal number system conversion
To convert octal number to hexadecimal number
follows the following steps:
a.
Write binary triple equivalent to each octal
number
b.
Now, again form the group of four digits from
right to left.
c.
Write respective hexadecimal number for each
binary group.
d.
Give the result
base 16.
Examples:
i. (236)8 = (?)16
|
Octal
number = |
2 |
3 |
6 |
|
Binary
equivalent = |
010 |
011 |
110 |
|
4
digits binary = |
1 0 01 |
1 1 1 0 |
|
|
Hexadecimal equivalent= |
9 |
E |
|
(236)8 = (9E)16
12. Hexadecimal to Octal number system conversion
To convert hexadecimal number to octal number
follows the following steps:
a.
Write binary equivalent 4 digits group to each
hexadecimal number.
b.
Now, again form the group of three digits from
right to left.
c.
Give the result base 8.
Examples:
i. (9A3)16 = (?)8
Hexadecimal
= 9 A 3
Binary
equivalent = 1001 1010
0011
3
digits binary = 100 110
100 011
Octal
equivalent = 4 6
4 3
(9A3)16 = (4643)8
Binary Calculation
Generally, there are four types of binary
calculation. They are:
1.
Binary Addition,
2.
Binary Subtraction,
3.
Binary Multiplication
4.
Binary Division.
1. Binary Addition
Binary addition is similar to decimal numbers addition.
Some rules for adding binary numbers are:
0 + 0
= 0
0 + 1
= 1
1 + 0
= 1
1 + 1
= 10 (Write '0' here, carry 1 to next column)
Example:
1 0
1 0
+
1 1
0 1
![]()
1
0 1
1 1
Hence, 1010
+ 1101 = 1 0
1 1 1.
2. Binary Subtraction
Binary subtraction is similar to decimal number
subtraction. Some rules for subtracting binary numbers are:
0 - 0
= 0
1 - 0
= 1
1 - 1 = 0
0 -
1 = 1 (with borrow 1 from the left column)
Example
1 0 1
1 1
-
1
0 1
![]()
1 0
0 1 0
Hence, 10 111 – 101 =
1 0 0
1 0.
3. Binary Multiplication
Binary multiplication is similar to decimal number
multiplication. Some rules for multiplying binary numbers are:
0×0=0
1×0=0
0×1=0
1×1=1
Example 1 0 0[1]
×
1 0 1
![]()
10
0 1
0
0 0 0
1 0 0 1
![]()
1
0 1 1 0 1
Hence 1001 ×101 = 101101
Binary Division
Binary division is similar to decimal number division.
Some rules for dividing binary numbers are:
0 ÷ 0 = 0
0 ÷ 1
= 0
1 ÷ 1
= 1
1 ÷ 0 = undefined
Example
ii. Divide 100101 by 110
Soln:
110)100101(110
-110
110
-110
X 1
- 0
1
:. Q=
110 R= 1
Concept of bits, bytes, nibble, and word
Bits
Bits stands for binary digits. It is the smallest unit of
information in computer. It represents 0 or 1.
Nibble
The combination of four bits is called a nibble.
Examples: 1001, 1000, etc.
Byte
The combination of eight bits is called a byte.
Examples: 10111101, 10110110, 10011110,
etc.
Word
Word is the combination of bits. It is the number of
bits that can process and transfer by the processor. Computers usually have a word
size of 8 bits, 16 bits, 32 bits, 64 bits, 128 bits, etc.
The different measurement units of
data in a computer are:
|
Bit = 1 or 0 |
1 Kilobyte =
1024byte |
1 Petabyte= 1024
TB |
|
1Crumb =2 bits |
1 Megabyte= 1024
KB |
1Exabyte = 1024 PB |
|
1 Nibble = 4 bits |
1 Gigabyte= 1024
MB |
1Zettabyte = 1024EB |
|
1 Byte = 8 bits or 2Nibble
or 1character |
1 Terabyte = 1024
GB |
1Yottabyte = 1024 ZB |





Comments
Post a Comment